Understanding Sports Medicine: A Comprehensive Guide is essential for athletes, coaches, and fitness enthusiasts. Sports medicine focuses on injury prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation, helping athletes recover safely while improving athletic performance. It combines orthopedic care, physical therapy, biomechanics, and sports nutrition to enhance strength, endurance, and overall well-being. Whether dealing with sports injuries or optimizing training techniques, this field plays a crucial role in keeping athletes at their best.
Pushing limits is part of the game, but without proper care, even minor injuries can lead to serious setbacks. Sprains, fractures, tendonitis, ACL tears, and concussions can disrupt an athlete’s career. The right mix of rehabilitation programs, strength training, and preventive strategies ensures long-term success. Staying ahead in sports isn’t just about talent—it’s about smart recovery and injury-free performance.
With Understanding Sports Medicine: A Comprehensive Guide, athletes gain expert insights into sports healthcare, biomechanics, recovery techniques, and performance enhancement. Whether you’re a beginner or a pro, learning about sports medicine specialists, injury management, and training optimization can help you build a healthier, stronger, and more resilient body.
What is Sports Medicine?

Sports medicine is a specialized field of healthcare focused on the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of sports injuries and the enhancement of athletic performance. Whether you’re a professional athlete, a weekend warrior, or someone engaging in physical conditioning, understanding sports healthcare is crucial for injury prevention and overall well-being.
Why is Sports Medicine Important?
- Reduces risk of injuries with proper preventive measures
- Optimizes athletic performance through structured strength training and sports nutrition
- Aids in faster recovery from sports injuries such as ACL tears, rotator cuff injuries, and stress fractures
- Supports long-term health by promoting biomechanics, physical therapy, and rehabilitation
Common Sports Injuries and Their Causes
Acute vs. Chronic Sports Injuries
Sports injuries fall into two broad categories:
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Injuries | Occur suddenly due to a direct blow, fall, or collision | Fractures, dislocations, ACL tears, concussions |
| Chronic Injuries | Develop over time due to repetitive stress or poor biomechanics | Tendonitis, shin splints, stress fractures |
Most Common Sports Injuries
Sprains and Strains
- Sprains: Injury to ligaments caused by overstretching
- Strains: Muscle or tendon injury due to overuse or improper movement
Fractures and Dislocations
- Fractures: Breaks in the bone from impact or stress
- Dislocations: Joint displacement that needs immediate sports medicine specialist intervention
Concussions and Head Injuries
- A traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by impact
- Symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, confusion, nausea
- Requires immediate medical evaluation
Tendonitis and Overuse Injuries
- Inflammation of tendons due to repetitive movement
- Common in runners, tennis players, and swimmers
Shin Splints and Stress Fractures
- Shin splints: Pain along the shinbone caused by excessive running
- Stress fractures: Small bone cracks due to repetitive impact
ACL Tears and Knee Injuries
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tears often occur due to sudden stops or pivots
- Requires ACL reconstruction surgery in severe cases
Rotator Cuff Injuries
- Shoulder muscle or tendon damage from repetitive overhead motion
- Common in baseball pitchers, swimmers, and tennis players
Preventive Measures for Sports Injuries
Warm-Up and Cool-Down Techniques
- Dynamic stretching before activity improves flexibility
- Static stretching after activity aids muscle recovery
Strength and Conditioning Training
- Resistance training improves joint stability
- Agility training enhances coordination and reduces injury risk
Proper Nutrition and Hydration
- Hydration is essential for preventing muscle cramps
- Sports nutrition with protein, omega-3s, and calcium strengthens muscles and bones
Correct Equipment and Technique
- Proper footwear and protective gear lower injury risks
- Biomechanical interventions help correct movement patterns
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sports Injuries
Medical History and Physical Examination
- Doctors assess previous injuries, movement limitations, and pain levels
Imaging Techniques
- X-rays: Detect fractures
- MRI scans: Identify ligament tears like ACL injuries
- CT scans and ultrasound: Analyze soft tissue damage
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation programs
- Pain management using corticosteroid injections
- Cryotherapy and compression therapy for inflammation
Surgical Interventions

- Arthroscopic surgery for ACL tears and rotator cuff injuries
- Bone fixation surgery for severe fractures
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Stages of Recovery
- Acute Phase: Pain control and swelling reduction
- Rehabilitation Phase: Restoring strength and function
- Return-to-Play Phase: Progressive reintroduction to activity
Physical Therapy and Muscle Strengthening
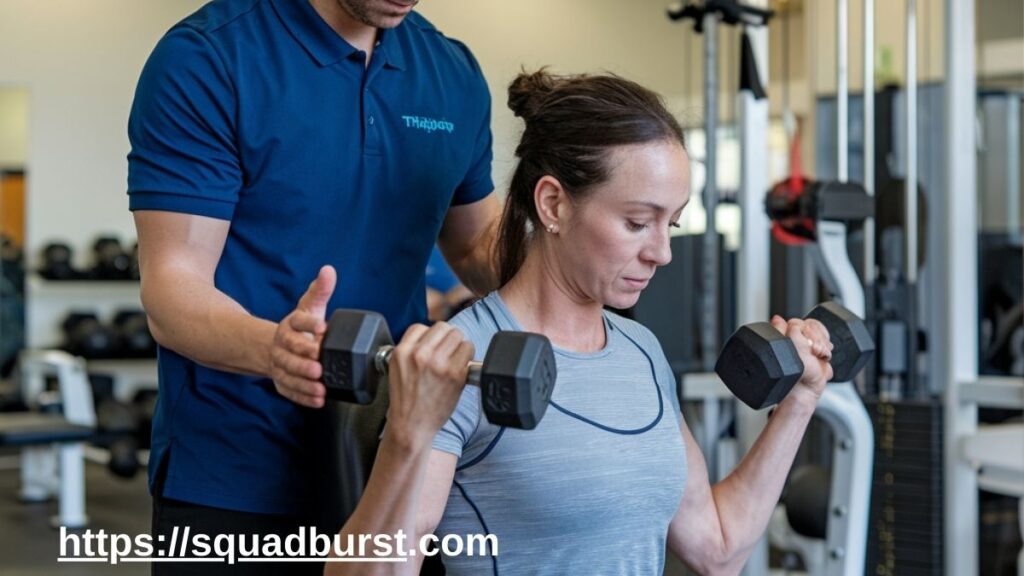

- Stretching and resistance training improve recovery
- Therapeutic exercises prevent re-injury
Mental Resilience and Sports Psychology
- Mental health support plays a vital role in recovery
- Stress management techniques help athletes regain confidence
Sports Medicine and Performance Enhancement
Strength Training and Conditioning
- Weightlifting and plyometrics boost muscle strength
- Speed training increases agility and quickness
Recovery Optimization
- Cryotherapy, massage therapy, and post-workout recovery techniques
- Sports nutrition with electrolytes, amino acids, and antioxidants
Biomechanics and Motion Analysis
- Gait analysis helps identify improper movement patterns
- Sports equipment design enhances injury prevention
Sports Medicine for Different Athletes
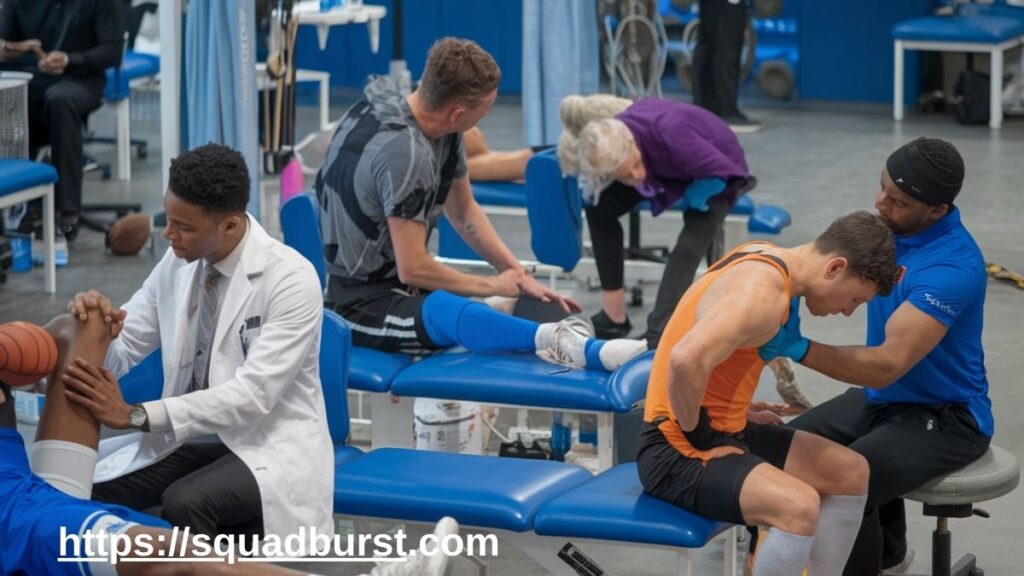

Sports Medicine for Different Athletes
Youth Athletes and Injury Risks
- Growth plate injuries require specialized care
- Early specialization increases overuse injury risks
Aging Athletes and Injury Prevention
- Bone health maintenance with calcium and vitamin D
- Joint-friendly exercises like swimming and cycling
Female Athletes and Unique Considerations
- Higher risk of ACL tears due to hormonal differences
- **Nutrition tailored to maintain bone density
FAQs
How do I know if my injury requires medical attention?
- Severe pain, swelling, or inability to move a limb requires urgent care
What’s the best way to speed up recovery?
- Physical therapy, hydration, and proper nutrition
Can sports injuries lead to long-term issues?
- Untreated injuries can cause chronic pain and joint degeneration
What’s the role of a sports medicine specialist?
- They diagnose, treat, and develop recovery plans for injured athletes
Is physical therapy necessary for minor injuries?
- Yes, it prevents re-injury and strengthens affected areas
Conclusion
Understanding Sports Medicine: A Comprehensive Guide helps athletes stay safe, recover faster, and perform better. It covers everything from injury prevention to rehabilitation and sports performance optimization. With the right training, nutrition, and medical care, athletes can reduce the risk of injuries and recover quickly when they happen. Sports medicine specialists use advanced treatments like physical therapy, biomechanics, and strength training to support long-term athletic health.
By following the principles in Understanding Sports Medicine: A Comprehensive Guide, athletes of all levels can train smarter and compete longer. Preventive care, proper technique, and recovery strategies are key to staying active and pain-free. Whether you’re dealing with sports injuries or looking to improve athletic performance, sports medicine offers proven solutions. With expert guidance, you can protect your body, enhance endurance, and achieve peak performance safely.

Emma Grace is a creative contributor to Squad Burst, blending her love for fashion and sports into captivating content. Her fresh perspective and relatable voice make her a favorite among readers who share her passion for style and athleticism.








